Risk Management Measures
Fundamental risk management policies
With the diversification of financial services and businesses, the risks to which banks are exposed are becoming more complex and diverse, heightening the importance of risk management. Hyakugo Bank is working to strengthen and enhance risk management. Its fundamental risk management policy is to gain an accurate understanding and awareness of each type of risk, and to establish an appropriate risk management framework to maintain the soundness and adequacy of management and secure stable income.
Comprehensive risk management system
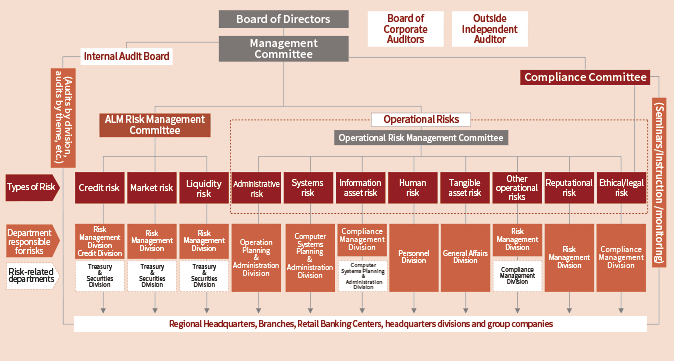
Hyakugo Bank has a comprehensive system to understand and manage the risks it faces in conducting its banking operations.
Specifically, risks are grouped into categories such as “credit risk,” “market risk” and “operational risk,” and some headquarters divisions are designated as having principal responsibility for managing a specific type of risk. In addition, the ALM Risk Management Committee and the Operational Risk Management Committee meet once a month to comprehensively gauge, evaluate and monitor the status of each risk and its management status, and consider risk management policies and measures, as well as submit major deliberation and reporting matters to the Management Committee and Board of Directors.
In addition, Hyakugo Bank quantifies risks according to consistent criteria and executes “comprehensive risk management” that controls the amount of risk within a scope appropriate to the Bank’s operating capabilities. Based on this approach, Hyakugo Bank sets limits for the amount of credit risk, market risk and operational risk, as well as for their total combined amount, in working to both maintain sound operations and generate stable earnings.
Moreover, by conducting internal audits through auditing units that are independent from business divisions, the Bank has established a mechanism for examining the appropriateness and effectiveness of management within each of its divisions and for encouraging improvement.
Risk Management System
Credit risk management
One of the most important management tasks for a bank is maintaining the soundness of loans and other assets.
Hyakugo Bank has therefore implemented a credit rating system that employs consistent criteria to evaluate the credit risk of each borrower and loan, and formulates lending policies and sets interest rates taking creditworthiness into account. In addition, the Bank has established a credit policy that limits the concentration of credit in any specific company, corporate group or industry, and strives to diversify risk associated with loans by understanding their distribution by industry, region, credit rating, credit amount and other categories from the standpoint of credit portfolio management.
Hyakugo Bank uses the Foundation Internal Ratings-Based (FIRB) approach to calculate the capital adequacy ratio, with the aim to develop an appropriate risk management structure to respond to diversification and sophistication of financial transactions and to enhance risk management.
In internal control, Hyakugo Bank uses Value at Risk (VaR) to measure credit risk in a way that includes credit concentration risk, which is not included in calculation of the capital adequacy ratio, based on a framework for integrated risk management. By managing risk within specified limits, the Bank aims to avoid overexposure and secure stable earnings.
In terms of its organizational structure, Hyakugo Bank has always clearly separated its sales promotion and credit investigation divisions to carry out rigorous assessment and control of credit risk.
For borrowers facing issues such as deteriorating business conditions, Hyakugo Bank appropriately determines management status and administers guidance for the formulation of revitalization plans as required to resolve problems and recover loans.
Market risk and liquidity risk management
The influence of changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, stock prices and other market movements on bank earnings has increased steadily. Consequently, Hyakugo Bank has strengthened its asset and liability management (ALM) capabilities with the objective of securing stable earnings. Specifically, the ALM Committee meets monthly to analyze the composition and changes in the composition of assets, such as loans and securities, and liabilities, such as deposits. The ALM Committee also provides consultation on optimal portfolio management based on future interest rate scenarios.
Hyakugo Bank handles market risk based on a framework for integrated risk management. The Bank quantifies various risks that are not included in the calculation of the capital adequacy ratio, such as interest rate risk embedded in its accounts, foreign exchange risk and stock price risk, primarily using VaR. We then control risk by setting risk limits for each type.
In its organization, Hyakugo Bank clearly separates trade execution (front office) and administrative processing (back office), and also has established a risk management department (middle office), thus creating a system of mutual checks and balances.
Hyakugo Bank deals with liquidity risk by appropriately monitoring and managing yen-denominated and foreign currency-denominated cash management, and maintains a fixed minimum level of highly liquid assets to prepare for contingencies. In addition, the Bank regularly confirms how much liquidity can be procured in the market and formulates measures in advance according to the tightness of credit.
Operational risk management
The environment in the financial industry is undergoing constant change, including diversification of businesses, products and services, and the systemization of business processing. Therefore, Hyakugo Bank sets operational risk management rules to comprehensively manage the risks accompanying its business operations.
The Operational Risk Management Committee, which meets once a month, comprehensively gauges, evaluates and monitors these risks, and conducts cross-organizational consultation on risk reduction measures, as well as submits major deliberation and reporting matters to the Management Committee and Board of Directors.
Hyakugo Bank considers operational risk to encompass a wide range of risks consisting of administrative risk, systems risk, information asset risk, ethical and legal risk, human risk, fixed asset risk, reputation risk, and other operational risks. The Bank is working to upgrade the level of both qualitative and quantitative risk management.
With regard to organization, a department is assigned responsibility for managing each type of risk, including administrative risk. Moreover, Hyakugo Bank has established a department controlling operational risks, thus creating a system of mutual checks and balances.
Administrative risk management
Hyakugo Bank is making efforts to establish stricter administrative protocols by drafting administrative regulations for all aspects of business operations, while improving and expanding in-house training, administrative instruction by headquarters, and internal audits. In addition, we engage in initiatives to reduce administrative risks through the improvement of administrative processes through means such as the introduction of systems and automation.
Systems risk management
Hyakugo Bank is working to prevent system malfunctions by conducting sufficient tests in advance when developing systems. We also prepare for emergency situations including system malfunctions and major natural disasters by duplicating infrastructure such as through the establishment of backup centers and formulating contingency plans.
(Reinforcement of cyber security management)
In order to maintain and enhance system security against the recent spate of increasingly serious cyber attacks, Hyakugo Bank has concluded a joint response agreement on cybercrime with the Mie Prefecture police, and became a member of Financial ISAC (*1), an external organization, as part of efforts to set up an early warning and preventive system through broad coordination of information. In addition, it also established Hyakugo Bank CSIRT (*2), a cross-sectional organization in April 2017, to reinforce its readiness both in normal and emergency situations.
*1
Information Sharing and Analysis Center. An organization for sharing cyber security information between various businesses.
*2
Computer Security Incident Response Team. An organization established in preparation for contingencies involving security problems including systems, which operates on a daily basis.
Information asset risk management
Hyakugo Bank takes all possible means to protect customer information and confidential business information by implementing various system security measures including measures to block unauthorized access, as well as thoroughly ensuring the proper handling of information assets among its directors and employees.
Reputational risk management
Hyakugo Bank has established a system for quickly responding to reputational risk by obtaining at an early stage information which could result in reputational risk including false reports and rumors. In addition, we are making efforts to enhance the understanding of and trust in the Bank through PR and IR activities.
Crisis management
In addition to these risk management systems, Hyakugo Bank, in light of the public nature of banking operations, has formulated the Business Continuity Plan, which will enable it to continue offering or resume at an early stage the necessary financial services to maintain the social and economic activities of the region, even in the event of a major disaster such as earthquakes or epidemics such as new strains of influenza. In addition, Hyakugo Bank is reinforcing its capability to respond to crises by formulating various contingency plans and conducting regular drills.

